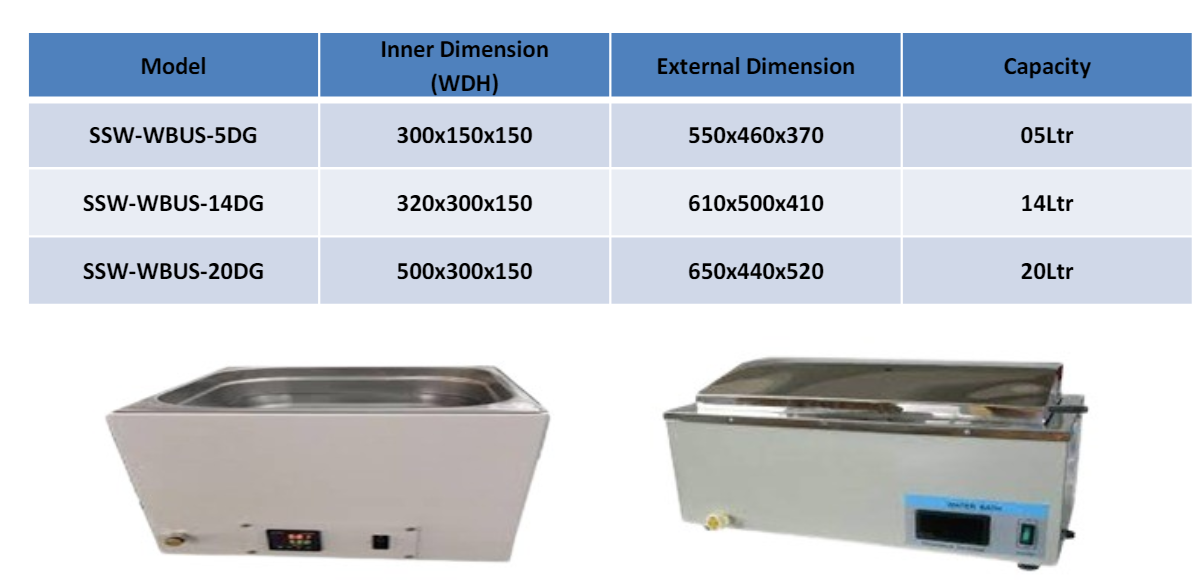
An unstirred water bath is a type of laboratory equipment used for maintaining a constant temperature of liquids or samples without agitation. Here are some key features and uses of unstirred water baths:
Design
Unstirred water baths typically consist of a container or bath filled with water, equipped with an electric heating element and temperature controls. The heating element is submerged in the water, and the temperature of the bath is regulated to maintain a stable temperature for the samples placed inside.
Temperature Control
They are designed to heat the water bath to a specific temperature set by the user. This temperature can often be adjusted with precision using digital controls or analog knobs.
Applications
Incubation
Unstirred water baths are commonly used in microbiology and molecular biology laboratories for incubating samples at a constant temperature.
Viscosity Measurements
They are also used in viscosity measurements, where maintaining a consistent temperature is crucial for accurate results.
Heat-sensitive Reactions
In chemical laboratories, they are utilized for heatsensitive reactions that require precise temperature control without agitation.
Capacity and Sizes
Unstirred water baths come in various sizes and capacities to accommodate different sample volumes and container sizes. They range from small benchtop units suitable for individual experiments to larger baths capable of holding multiple containers or larger vessels.
Features
Many modern unstirred water baths include safety features such as over-temperature protection and alarms to prevent overheating of samples. Some models may also have insulation to improve energy efficiency and maintain temperature stabilitySpecification: